FAQs
-
What is the battery internal resistance?
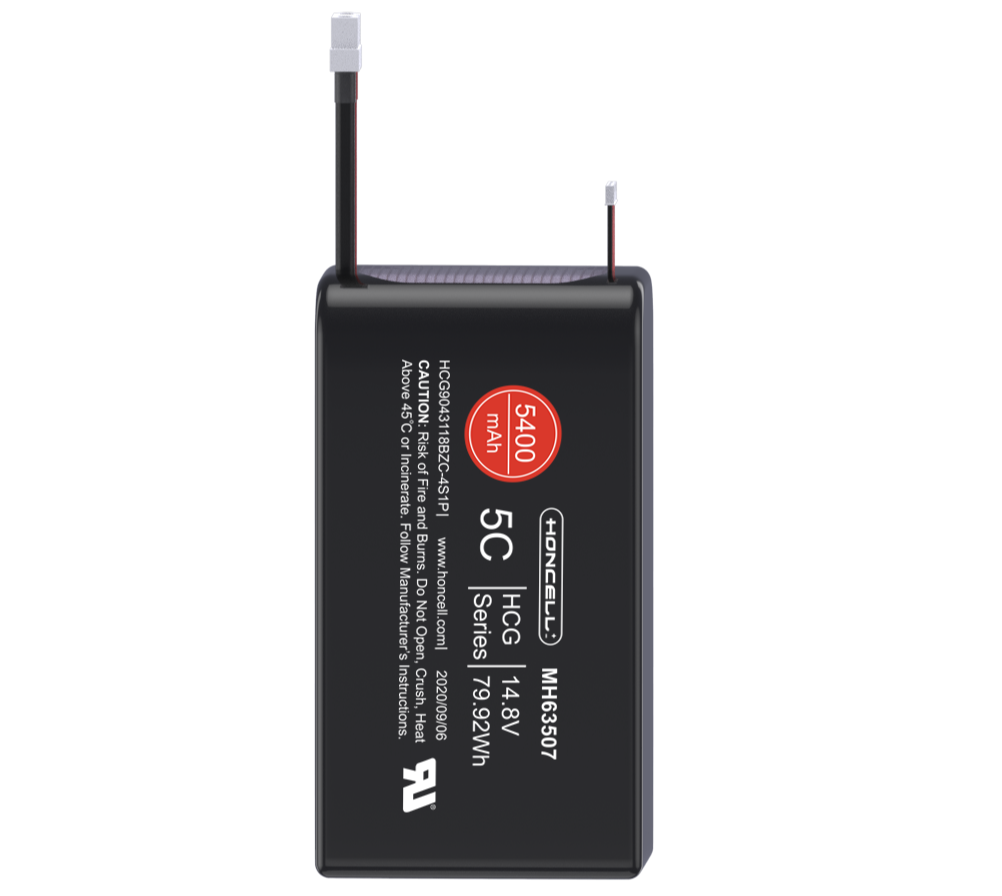
One of the urgent requirements of a battery for digital applications is low internal resistance. Measured in milliohms (mΩ), the internal resistance is the gatekeeper that, to a large extent, determines the runtime. The lower the resistance, the less restriction the battery encounters in delivering the needed power bursts. A high mΩ reading can trigger an early 'low battery' indication on a seemingly good battery because the available energy cannot be delivered in an appropriate manner. In HONCELL, we produce the massive Li-ion polymer batteries with little internal resistance. Please refer to our specified datasheet of each model for details of its resistance.
-
Where Li-ion polymer batteries should be stored?
Li-ion polymer batteries should be stored in a place not exposed to direct sunlight. Make sure the area is dry and has minimal temperature variation. Storage in areas subject to high temperatures, humidity or rain may cause deterioration in battery quality and durability. To avoid short circuiting batteries during storage, be sure that the positive and negative terminals do not come in to contact with each other.
-
What is nominal capacity?
Nominal capacity refers to the least capacity that should be discharged under certain charging or discharging condition. For example, the nominal capacity for HCP603450 is 1000mAh, it means when this battery is charged with 0.1C=100mA for 16 hours, rest 1~4 hours, then discharge with 0.2C=200mA to 3.0V, the capacity discharged should be no less than 1000mAh (Ambient temperature: 20±5℃).
-
What problem will occur when mixed use batteries of different capacities and different voltages?
When mix use batteries of different capacities and different voltages, leakage or short circuit may occur. These problems occurred because some of the batteries will be over charged and some others are not charged to full capacity. When these batteries are discharged together, the batteries with full capacity cannot be fully discharged while the other batteries with low capacity will be over discharged. In this way, the batteries will be damaged and leakage or short circuit low (zero ) voltage will occur.
-
How over discharge affect battery characteristics?
After the battery has been fully discharged and voltage lowers to the designated value, if we continue to discharge the battery, the battery will be over discharged. We usually set the cut-off voltage according to the discharging current. We often set cut-off voltage as 3.0V (Lipo cell) for battery with 0.2C-1C (normally) discharge current. Over discharging batteries, especially with large current, can bring disastrous results; over discharging batteries once and again will cause even worse result. Generally speaking, over discharging will cause battery’s internal pressure to rise, damage activity of positive electrode and negative electrode substance, decreasing battery's capacity.
-
What are the possible reasons for zero voltage or low voltage?
1. When batteries are short circuit from outside or over discharged/over charged or charge reverse.
2. When battery is continuously charged with high current, the electrode swells so that the two electrodes contact directly, short circuit is caused.
3. Batteries are short circuit or slightly short circuit from inside. Ex. There is spur on positive electrode or negative electrode, which gets through the insulator causing short circuit; Positive electrode and negative electrode are placed inappropriately and electrodes contact each other, causing short circuit; Positive electrodes contact directly with steel case, causing short circuit; Powder on negative electrode drops into the insulator or insulator fails to work well so that positive plates contact negative plates, causing short circuit. -
What is penetration test?
After the battery is fully charged, penetrate the battery from the center of it with a nail Ф2.5mm-5mm and let it stay inside, the battery should not explode or got fire.
-
What is temperature rising test?
Charge the battery to full capacity and put it into the oven, increasing the temperature every 5 minutes until the temperature of the oven inside reaches 150℃, keep 150℃ for 10 minutes, the battery should not explode or got fire.
-
What is temperature cycling test?
Temperature Cycling Test includes 27 cycles. Every cycle includes the following steps:
1. Take the battery from normal room temperature environment into the environment with 66+/-3℃, 15+/-5% and rest for one hour.
2. Transfer the environment to be 33+_3c 905%, rest the battery for one hour.
3. Transfer the environment to be 403% rest the battery for one hour.
4. Rest the battery for 0.5 hour under 25C.
The above four steps make up a whole cycle. After 27 cycles, the battery should not leak, be rusted or have other abnormal results.