Handling Precautions
This document applies to Honcell Energy's Li-ion Polymer Rechargeable Batteries. Contact Honcell for non-standard applications. Honcell is not responsible for accidents under unapproved conditions. Any necessary improvements will be communicated in writing.
-
1. Charge
-
2. Discharge
-
3. Protection Circuit Module (PCM)
-
4. Storage
-
5. Handling of Cells
-
6. Prohibitions
-
7. Battery Disposal
-
-
1.1 Charge
Always use a charger specifically designed for Li-ion polymer batteries; never use other types of chargers to charge the LiPo batteries. Failure to do so can damage the batteries, leading to potential fire hazards and personal injury.
-
1.2 Charge Current
The charging current should be less than the maximum charge current specified in the datasheet. Charging with a higher current than the recommended value may cause damage to the cell's electrical, mechanical, and safety performances, potentially leading to heat generation or leakage.
-
1.3 Charge Voltage
Charge within the specified voltage range as per the datasheet. Strictly avoid surpassing the maximum voltage limit to prevent damage to the cell's electrical and safety functions, such as heat generation or leakage. Charger design must adhere to this limitation.
-
1.4 Charge Temperature
The battery shall be charged at between 0 and 45℃.
-
-
-
2.1 Discharge Current
The cell should be discharged at a rate lower than the maximum discharge current specified in the datasheet. High discharge currents may significantly reduce discharge capacity or lead to overheating. If intending to discharge the battery at a current higher than the specified maximum, please consult us, especially for the HCG series (high C-rate batteries).
-
2.2 Discharge Temperature
The standard cell shall be discharged within the range of -20 to 60℃. For low-temperature or high-temperature batteries, please refer to the related datasheet for specific discharge temperature guidelines.
-
2.3 Over-discharge
The cell may self-discharge into an over-discharged state if unused for long periods, affecting performance. To prevent this, periodically charge and maintain voltage between 3.7V to 3.9V. Chargers must include safeguards: a pre-charge at low current (0.01C) for 15-30 mins, followed by rapid charge once individual cell voltage exceeds 3.0V in 15-30 mins. If not, the charger should halt further charging, indicating an abnormal state.
-
-
-
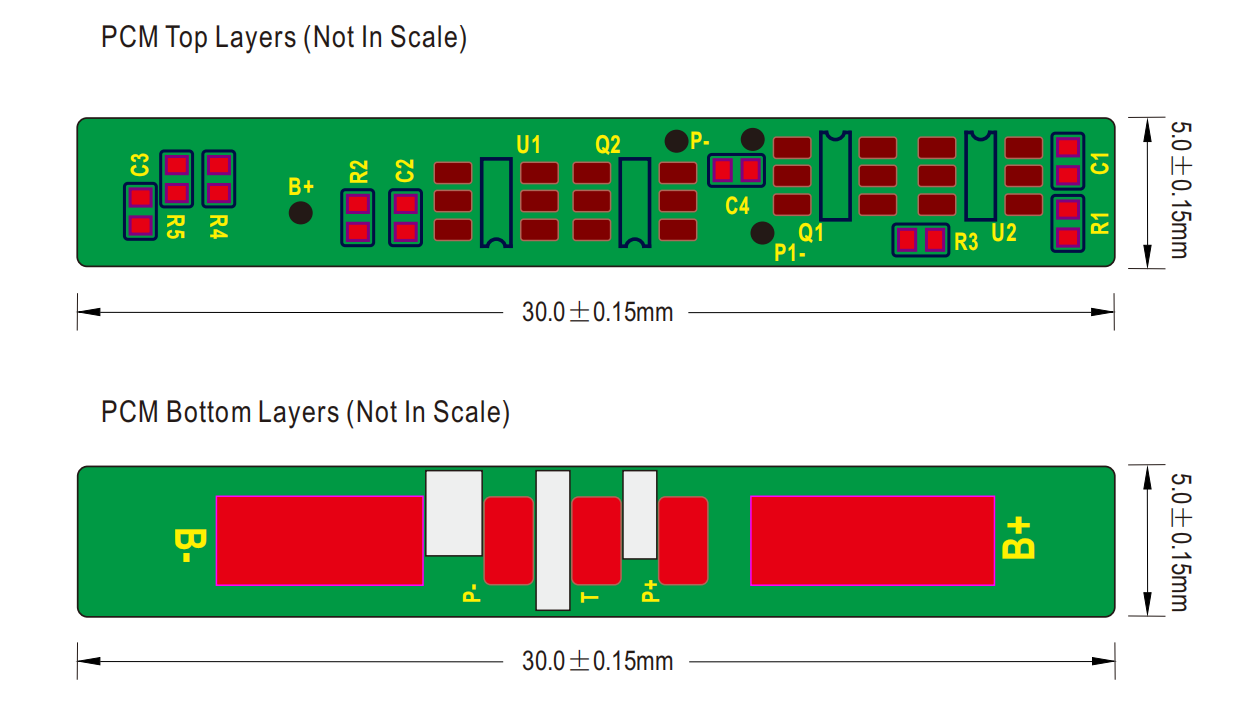
3.1 Protection Circuit Module (PCM)
The cell or battery pack shall be protected by a PCM with functions for overcharge, over-discharge, over-current, and short-circuit protection. This ensures safety and prevents significant deterioration of cell performance.
-
3.2 Overcharge Protection
The overcharge protection function shall halt charging if any cell in the battery pack reaches overcharge protection voltage.
-
3.3 Overdischarge Protection
The overdischarge protection function is designed to prevent a further drop in cell voltage to overdischarge protection voltage or less per cell in any cell of the battery pack. It is recommended that the dissipation current of the PCM be minimized to 0.5uA or less to enhance overdischarge prevention. The protection function monitors each cell of the battery pack and maintains constant current control at all times.
-
-
-
4.1 Storage
Store the batteries in a cool and well-ventilated area away from heat sources, open flames, corrosive chemicals, food, and drinks. Since a short circuit can cause fire, heat, burns, leakage, and rupture, keep batteries in their original packaging until use and do NOT jumble them.
Maintain the cells in a half-charged state, around 50%. Store the cells/battery pack at temperatures between -20 to 50°C. If the cells/battery packs will be stored unused for three months or longer, transfer them to a dry and cool place.
It is highly recommended to activate the battery at least once every three months following these steps:
(1) CC/CV charge @ 0.2C to 4.2V, then rest for 5 minutes.
(2) CC discharge @ 0.2C to 3.0V, then rest for 5 minutes.
(3) CC charge again @ 0.2C to 3.9V.
The voltage for long-term storage should be within the range of 3.7V to 3.9V. The preferred environmental conditions include an ambient temperature of 23±2°C, relative humidity between 45-75% RH, and a pressure of 86-106 kPa.
-
-
-
5.1 Handling of Cells
(1) Avoid short-circuits to prevent overheating and loss of function.
(2) Keep cells away from sharp objects during handling and storage.
(3) Prevent assembly errors by avoiding contact between positive and negative leads.
(4) Protect cells from mechanical shocks.
(5) Prevent electrostatic discharge during use, charging, and storage.
(6) Avoid contact with metal conductors like neck chains or bolts.
(7) Do not bend or fold the sealing edge.
(8) Do not open folded edges on cell sides.
(9) Do not bend tabs.
(10) Avoid extreme environments like ovens or high-voltage containers.
(11) Use only certified chargers.
(12) Do not use metal conductors to connect positive and negative leads.
(13) Store batteries to prevent terminal short circuits.
(14) Keep batteries away from heat sources and direct sunlight.
(15) Immediately stop charging if the cell shows signs of overheating, odor, color changes, or deformities.
(16) Supervise children using batteries.
(17) Read and understand Handling Precautions and Safety Guidelines before use.
(18) Keep batteries away from children.
(19) Store batteries within specified conditions in this specification sheet.
-
5.2 Soft Aluminum Foil
(1) Don't strike the battery with any sharp-edged parts.
(2) Trim your nails or wear gloves before handling the battery.
(3) Clean the worktable to ensure no sharp particles are present.
-
5.3 Sealed Edge
(1) The sealing edge is very delicate.
(2) Don't bend or fold the sealing edge.
-
5.4 Folding Edge
(1) The folding edge is formed during the battery process and has passed all hermetic tests.
(2) Don't open or deform the folding edge.
-
5.5 Tabs
(1) The battery tabs are not very resilient, especially the aluminum tab.
(2) Don't bend the tabs.
-
5.6 Mechanical Shock
Avoid dropping, hitting, or bending the battery body.
-
-
-
6.1 Prevention of Short Circuit
Ensure sufficient insulation layers between wiring and cells for additional safety protection.
-
6.2 Prohibition of Disassembly
Never disassemble the cells. If a battery is unintentionally crushed, releasing its contents, use rubber gloves to handle all battery components. Avoid inhaling any emitted vapors.
(1) Disassembling may generate internal short circuits in the cell, leading to gassing, firing, or other issues.
(2)Electrolyte is harmful. Li-po batteries should not have liquid electrolyte flowing. If materials from a damaged or ruptured cell contact you:
a. Eye contact: Wash immediately with plenty of water and soap for at least 15 minutes.
b. Skin contact: Wash immediately with water and soap.
c. Inhalation of vented gas: Remove to fresh air.
d. Ingestion: Seek medical attention immediately.
-
6.3 Prohibition of Dumping Cells into Fire
Never incinerate or dispose of cells in fire to prevent firing.
-
6.4 Prohibition of Cells Immersion into Liquid
Cells should never be soaked in liquids such as water, seawater, soft drinks, juices, coffee, or others.
-
6.5 Battery Cells Replacement
Battery replacement should be carried out only by authorized parties and not by users.
-
6.6 Prohibition of Use of Damaged Cells
Cells may be damaged during shipping. If any unusual features such as deformation, the smell of electrolyte, electrolyte leakage, or others are found, the cells should not be used. Cells with a smell of electrolyte or leakage should be placed away from fire to avoid firing.
-
-
-
7.1 Battery Disposal Instructions
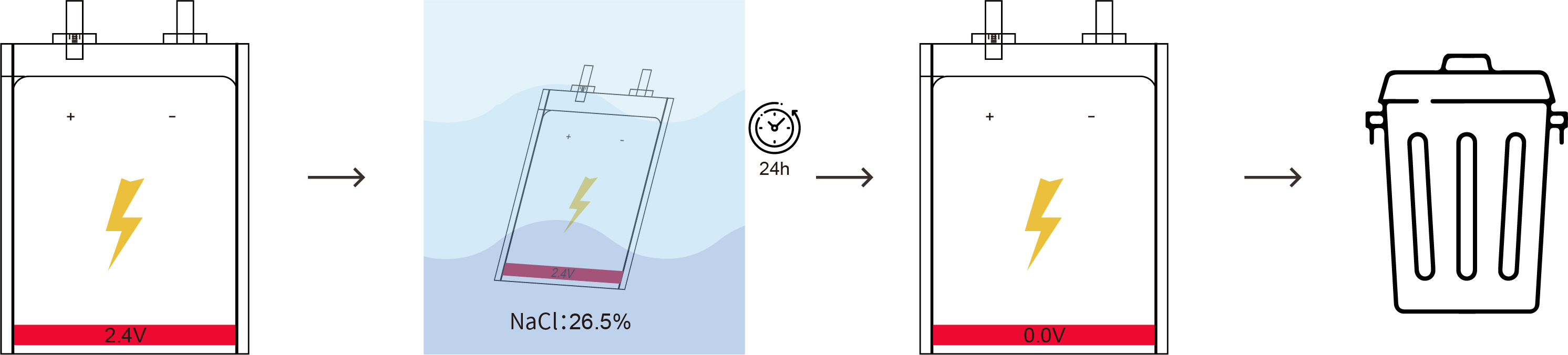
(1) Discharge the battery pack to 2.5V per cell or less.
(2) Fill a bucket with enough water to completely submerge the battery pack.
(3) Add salt to the water until no more salt will dissolve, and the water is fully saturated.
(4) Place the battery pack in the bucket, ensuring it is fully submerged in the saltwater solution for 24 hours.
(5) Remove the battery pack from the saltwater and test the voltage.
(6) If the voltage does not read 0.0V, repeat the submersion and re-test until the voltage reaches 0.0V.
(7) Once the battery pack has been discharged to 0.0 Volts, it is safe to dispose.
Please note: Follow these steps carefully for the proper and safe disposal of the battery pack.
-